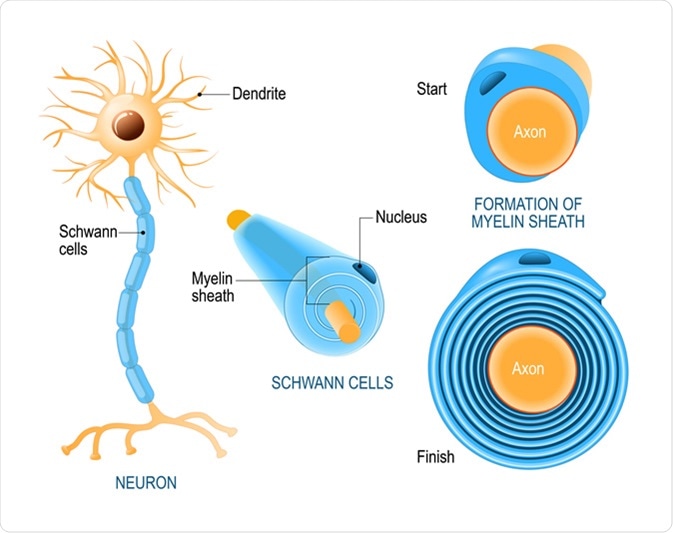
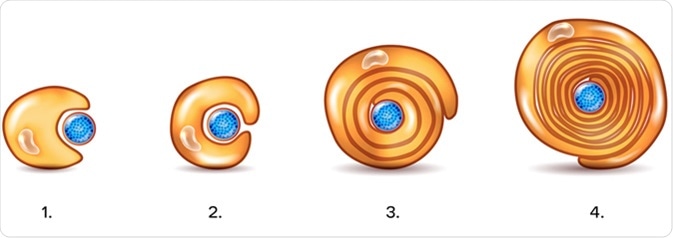
Describe How the Schwann Cells Form the Myelin Sheath
The myelin sheath surrounds and insulates the axon. These cells that form myelin protect support and maintain equilibrium in your nervous system are called glial cells.

Schwann Cells Biology Dictionary
Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers.

. Outside the myelin sheath there is a cellular layer called the neurilemma. Schwann cells supply myelin sheaths for axons but they are found in the PNS instead of the CNS. The axon is surrounded by a whitish fatty layer called the myelin sheath.
The term neurite is used to describe either a dendrite or an axon. Oligodendrocytes have the primary function of helping in the movement of information along axons. CNS and PNS myelin differ in several important ways.
This point of view was supported by the observation that not only Schwann cells but also. This coating enables the electrical impulses between nerve cells to travel back and forth rapidly. Myelin is made by oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system CNS and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system PNS.
The sheaths are formed by glial cells. In analogy to the Schwann cells of the PNS The cell body not the branches of the oligodendrocytes exists predominantly in the white matter less frequently in the gray matter. Aid in regeneration of damaged nerve fibers.
When myelin becomes damaged these electrical signals are interrupted and may even stop altogether. Oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system. 1 Composed on many layer of cell membrane with no cytoplasm between them 2 Loose covering around the entire length of the dendrite 3 Produced by Schwann cells 4 Produced by astrocytes 5 Composed of a single layer of cell membrane with cytoplasms and nuclei.
The remaining bulk of the. What statements best describe the myelin sheath. One oligodendrocyte forms myelin sheath segments for several neurons whereas a single Schwann cell myelinates one segment for a single neuron.
Endothelial cells line the inside of every blood vessel in the body. DiFiores Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations 11th Ed. The consequences of deleting CMTM5 and CMTM6 in oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells respectively may appear roughly.
The main job of endothelial cells is to provide a barrier between the blood and the rest of. Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord. The elaboration wrapping and compacting of myelin membrane to form myelin sheaths are similar in myelinating OPCs during development and in remyelinating OPCs during the regenerative process.
They are also commonly known as. The sheath enables action potentials to travel faster than in unmyelinated axons of the same diameter whilst using less energy. The nerve enters the capsule at one pole which might be out of the plane of section and therefore not visible with its myelin sheath intact but then it is quickly lost.
Satellite cells seem to regulate the surroundings around nerve cells keeping chemicals in a state of equilibrium. Describe location an function of Ependymal cells. The myelin sheath is the protective fatty coating surrounding your nerve fibers similar to the protective insulation around electrical wires.
However we recently found the paralog CMTM6 to be expressed in myelinating Schwann cells in which it is involved in the previously unknown function of Schwann cells to restrict the diameters of peripheral axons Eichel et al 2020. Form neurilemma around all PNS fibers and myelin around most of them. Secrete and circulate CSF.
Describe location an function of Microglia cells. Neuroglia outnumber nerve cells by a ten to one ratio in. In the peripheral nervous system Schwann cells are neuroglia cells that support neuronal function by increasing the speed of impulse propagation.
The unmyelinated portion of the axon extends toward the opposite pole from which it entered and its length is covered by flattened Schwann cell lamellae that form the inner core of the corpuscle. However some differences between myelination and remyelination. Describe location an function of Schwann cells.
The degeneration of the myelin sheath which is formed by oligodendrocytes is a characteristic morphological change in the disease multiple sclerosis. The myelin sheath in.

Compact Myelin Sheaths Are Required For Nervous System Function Download Scientific Diagram
What Is The Relationship Between Schwan Cells And Myelin Sheaths Quora
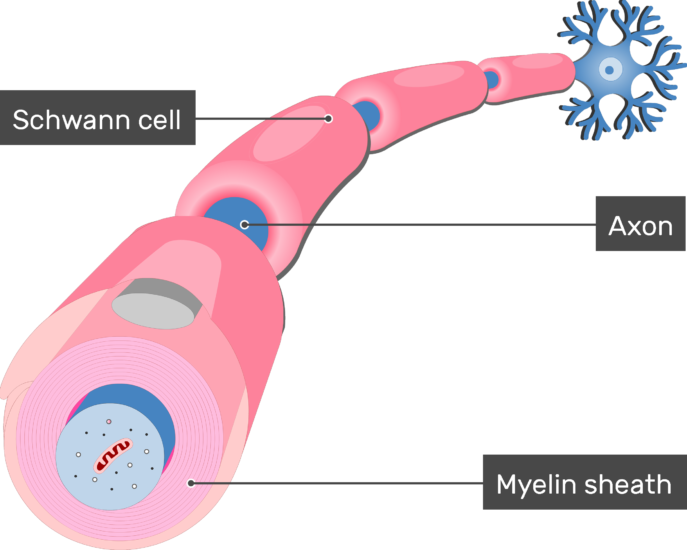
Myelination Of Axons By Schwann Cells
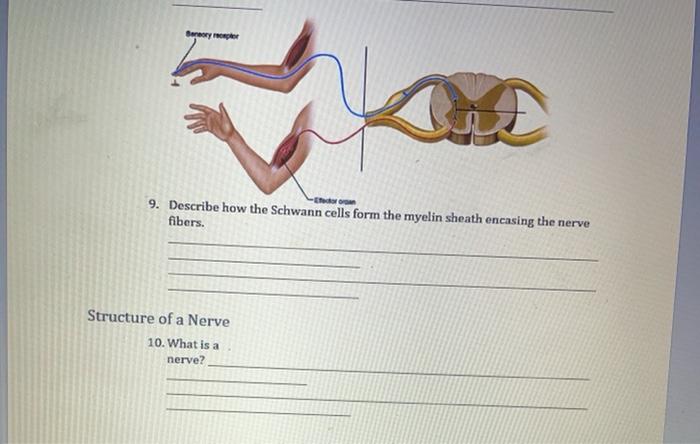
Solved Sanary Oper Id 9 Describe How The Schwann Cells Chegg Com

Lesson Explainer Nerve Cells Nagwa

What Is Myelin From A Structural Perspective Where Does The Schwann Cell Component End And The Fatty Acids Begin Quora
What Is The Difference Between Schwann Cell And Myelin Sheath Pediaa Com

Regulation Of Schwann Cell Myelination And Dedifferentiation A Download Scientific Diagram

Difference Between Oligodendrocytes And Schwann Cells Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

What Is The Role Of Neuron Schwann Cells Quora
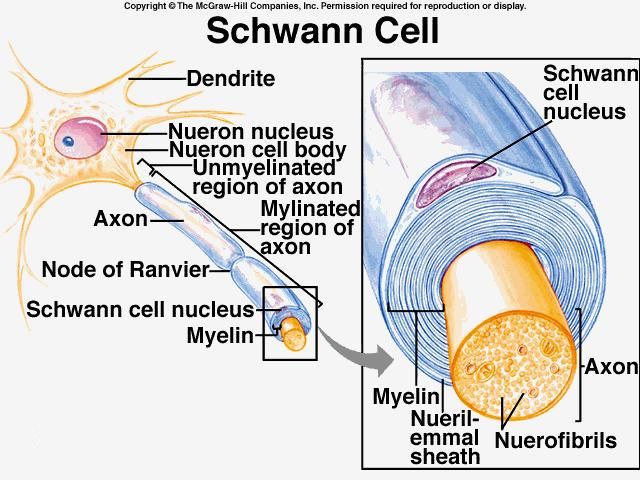
In Human Anatomy What Is The Purpose Of The Schwann Cells Socratic

Myelin Biochemistry Britannica

Histology Of The Peripheral Nerves And Light Microscopy Nysora Nysora

Schwann Cells Function Simply Psychology
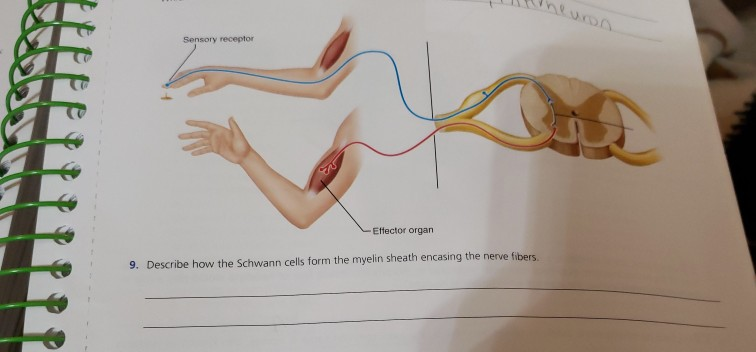
Solved Sensory Receptor Effector Organ 9 Describe How The Chegg Com

Question Video Describing The Structure Of The Myelin Sheath Nagwa
Comments
Post a Comment